directive
Directives are like directions, but can be grouped together with attributes for convenience. This is typically used for tempo markings at the beginning of a piece of music. This element has been deprecated in Version 2.0 in favor of the directive attribute for direction elements. Language names come from ISO 639, with optional country subcodes from ISO 3166. |
Element Information
Model
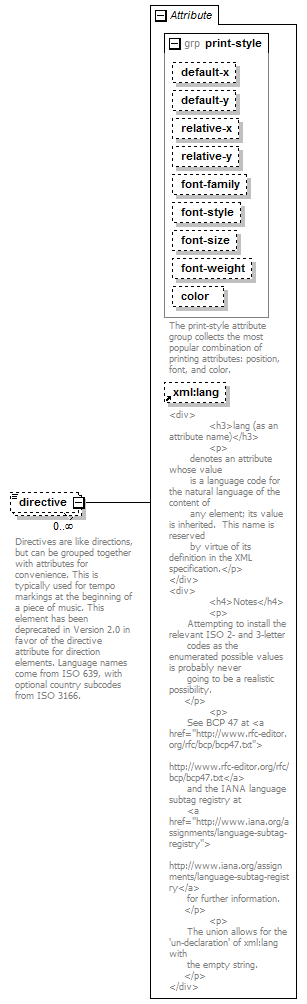
Attributes
| QName | Type | Fixed | Default | Use | Inheritable | Annotation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| color | color | optional | |||||
| default-x | tenths | optional | |||||
| default-y | tenths | optional | |||||
| font-family | comma-separated-text | optional | |||||
| font-size | font-size | optional | |||||
| font-style | font-style | optional | |||||
| font-weight | font-weight | optional | |||||
| relative-x | tenths | optional | |||||
| relative-y | tenths | optional | |||||
| xml:lang | union of(xs:language, restriction of xs:string) | optional |
|
Source
<xs:element name="directive" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"> <xs:annotation> <xs:documentation>Directives are like directions, but can be grouped together with attributes for convenience. This is typically used for tempo markings at the beginning of a piece of music. This element has been deprecated in Version 2.0 in favor of the directive attribute for direction elements. Language names come from ISO 639, with optional country subcodes from ISO 3166.</xs:documentation> </xs:annotation> <xs:complexType> <xs:simpleContent> <xs:extension base="xs:string"> <xs:attributeGroup ref="print-style"/> <xs:attribute ref="xml:lang"/> </xs:extension> </xs:simpleContent> </xs:complexType> </xs:element> |