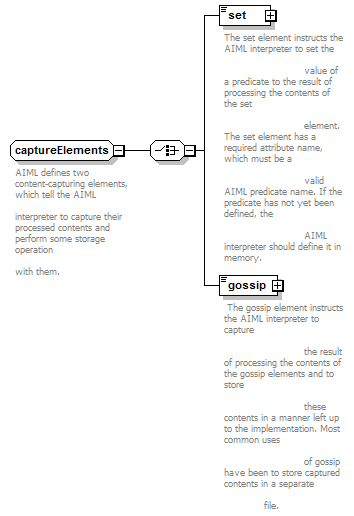
<xs:group name="captureElements">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>AIML defines two content-capturing elements, which tell the AIML interpreter to capture their processed contents and perform some storage operation with them.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:choice>
<xs:element name="set">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The set element instructs the AIML interpreter to set the value of a predicate to the result of processing the contents of the set element. The set element has a required attribute name, which must be a valid AIML predicate name. If the predicate has not yet been defined, the AIML interpreter should define it in memory.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:complexContent>
<xs:extension base="MixedTemplateContentContainer">
<xs:attribute name="name" type="PredicateName"/>
</xs:extension>
</xs:complexContent>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="gossip" type="MixedTemplateContentContainer">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The gossip element instructs the AIML interpreter to capture the result of processing the contents of the gossip elements and to store these contents in a manner left up to the implementation. Most common uses of gossip have been to store captured contents in a separate file.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
</xs:choice>
</xs:group> |